
By Jennifer Chan
Also read:
How Much Does it Cost to Advertise on Google?
Is Google AdWords Worth it for My Small Business
You’ve considered the pros and cons of using Google AdWords for your small- or medium-sized business (AdWords is a great way to get high-quality leads; AdWords is a great way to accidentally spend a lot of money). If the pros outweigh the cons, you’re ready to dive into the “how” of advertising on Google. As you start exploring the Google AdWords platform, you’ll need to know the language. Below are the 13 (plus one) Google Search Network terms you should understand before you start creating ads.
Glossary for Google AdWords

Account: Start by creating a Google AdWords account. You'll need all of your business information and a credit card.
Campaign: Create ad campaigns within your Google account. For each campaign, you can set your daily budget, location targeting, scheduling, the network your ads will appear on and more.
Ad Group: Campaigns consist of one or more Ad Groups. Each Ad Group contains Ad Group-specific keywords and one or more ads.
Extended Text Ad: This is the default ad format. All Search Network ads are text-only.
Keywords: Phrases, selected by you, that trigger your ad to appear. Keyword lists might include the name of your company, your product, your service plus your town, etc.
Keyword Match Types: Each keyword has a match type. There are five main match types.
- Broad match: Google considers your keyword as an indicator. Your ad will show when a user searches for related concepts.
- Broad match modifier: By placing a “+” in front of any word in a broad match keyword phrase, you tell Google to only show ads to users who have included that word in their search.
- Phrase match: Ad will show when a user inputs the actual words of the keyword phrase. Search can be in any order and may include additional words.
- Exact match: Ad will only show when a user searches for the exact words in the keyword phrase.
- Negative: Negative keywords are words or phrases for which you do not want your ad to be shown.
Quality Score: Google rates how well it thinks your keywords, ads and campaign will serve the user. Quality score is a factor in the auction.
Auction: Which ad gets shown to which user is determined by auction every time an ad is shown. When a user types words into Google’s search engine bar, Google takes a nanosecond to compare all of the ad campaigns vying for placement for those keywords. The auction winners are rewarded with the top spots on the search engine results page (SERP).
Read more on how the auction works
Impressions: The number of times your ad has appeared in a given time frame.
Clicks: The number of times your ad has been clicked on in a given time frame.
Cost-Per-Click (CPC): The average amount you have paid in a given time frame when your ad is clicked on.
Click-Through Rate (CTR): The rate at which users who have seen your ads click on them.
Keyword Planner: A free tool offered by Google to help you find keywords and estimate how well they might work for your campaign.
Location Targeting: Tell Google to only show ads in a certain location. This can be determined by country, state, city, zip code or pinpointing the location on a map.
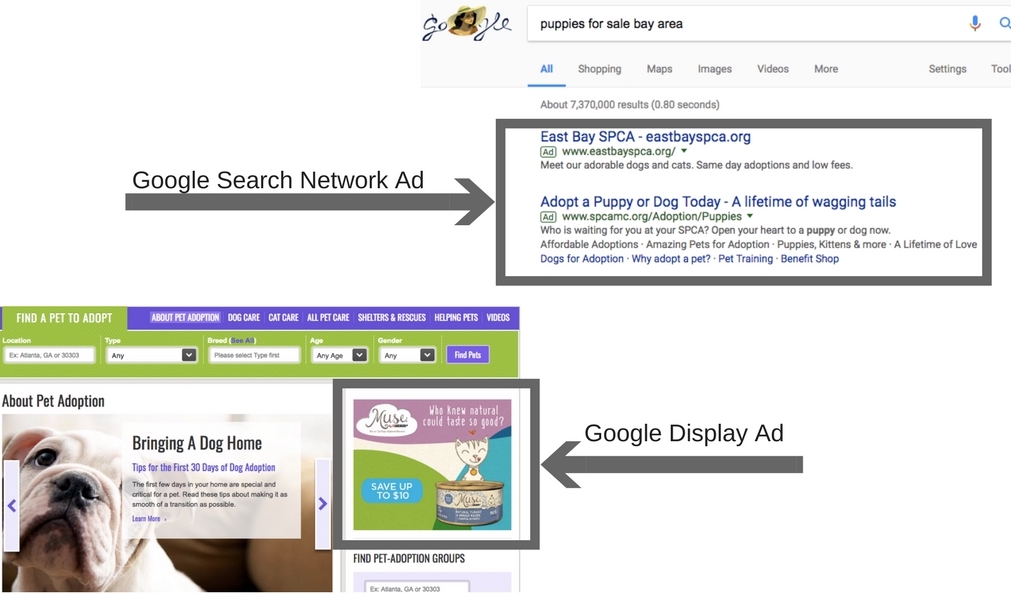
Note: Most small businesses should start by advertising on the Google Search Network. Search Ads show on Google’s SERP. Display Ads show on Google’s affiliate pages. For more on choosing a campaign type, click here.
If you’re interested in running AdWords for your business but don’t have the know-how or time, we’d love to do it for you. Email us or call us at (707) 575-5373.
To read more of Jennifer Chan's work, check out her writing for the Diamond Certified Blog.
